The ecosystem complexity and varying forest structures of mangrove forests limit mangrove carbon stock assessments to traditional in-situ methodologies. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that remote sensing techniques, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), can effectively map mangrove biomass over larger areas. A new study published by Basyuni et al. (2025) integrated remote sensing models with Lorey’s height measurements, which was then complemented with UAV imagery and in-situ measurements, to assess mangrove aboveground biomass (AGB) in Budeng–Perancak, Bali, Indonesia. Findings show that accurate and efficient UAV methods can provide reliable AGB data over time. This can further improve the accuracy of greenhouse gas inventory and carbon storage estimates.
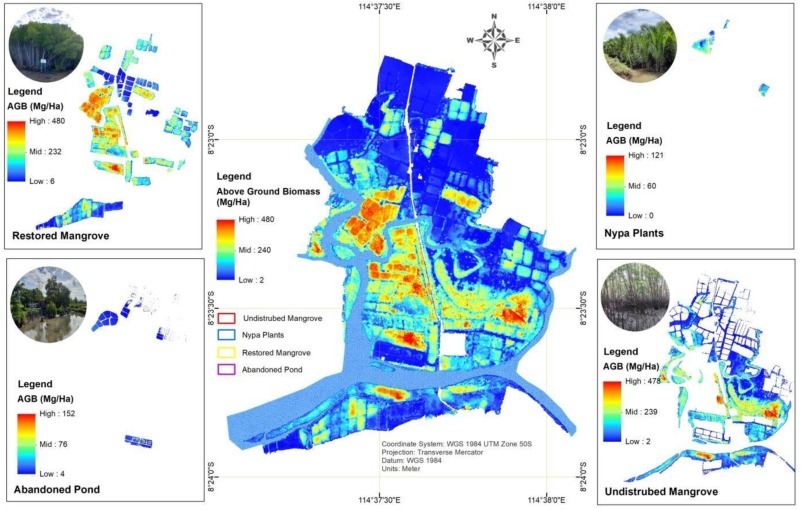
Read the study here: Mangrove aboveground biomass estimation using UAV imagery and a constructed height model in Budeng–Perancak, Bali, Indonesia

